Understanding Commercial Insurance
Commercial insurance is a type of comprehensive policy used by business owners to protect organizations from various financial losses. Losses include things like property damage, theft, workplace injuries, liability claims, and much more. Oftentimes commercial insurance policies are bundled to include a variety of different coverage types. These comprehensive policies are often referred to as business owner’s policies (BOPs) and they typically include:
- Property Insurance: Provides coverage for damage to equipment, buildings or any other assets owned by a business. Typical accidents covered include fires, theft and natural disasters.
- Liability Insurance: Protects companies from any claim involving injuries or property damages caused by the businesses employees, products or operations.
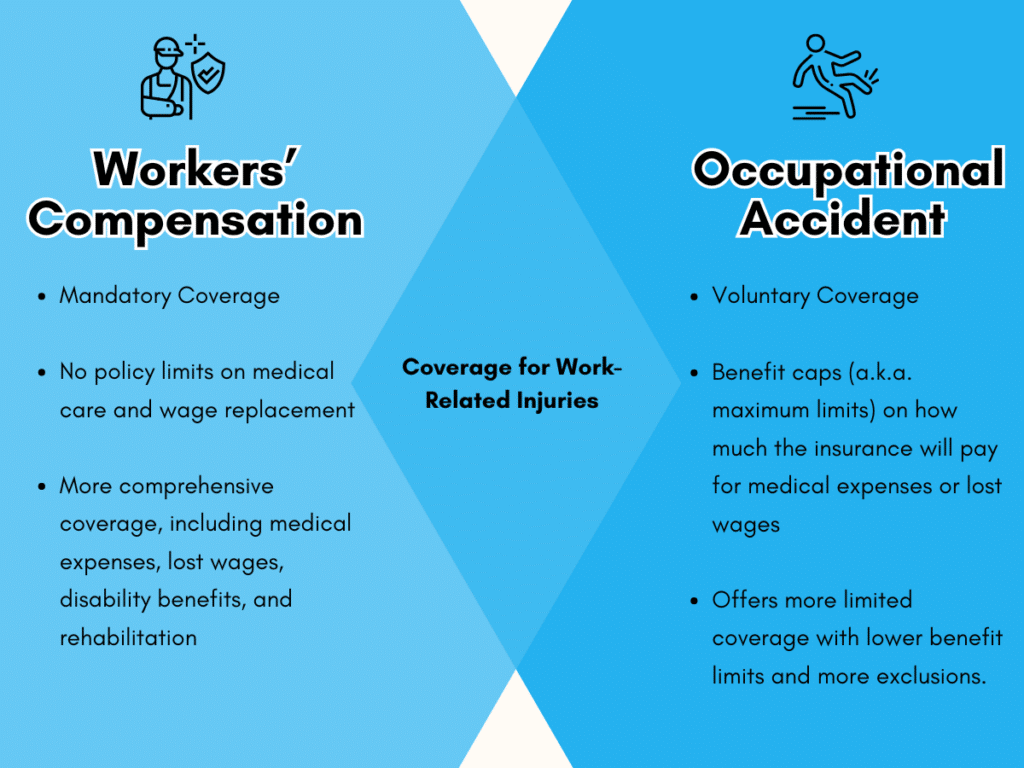
- Workers’ Compensation: Covers the medical costs and a portion of lost wages to employees who get injured or sick on the job.
- Business Interruption Insurance: If a business is forced to close down temporarily, this coverage will provide compensation for lost income. Examples of reasons a business might need to close down are natural disasters, or fires.
There are also other more specialized types of commercial insurance that can be crucial depending on the industry you work in. These include professional liability insurance and cyber liability coverage. Additionally, companies that regularly use vehicles in their daily operations need specialized coverage too. This is where commercial auto insurance comes into play.
What is Commercial Auto Insurance?
Commercial auto insurance is designed to protect vehicles used for business purposes. Unlike personal automobile coverage, it covers a broader range of business-related risks.
For example, if you have a fleet of freight trucks, delivery trucks, use your personal vehicle for work purposes, or have staff driving company
- Company-owned vehicles being used for deliveries or client visits.
- Any personal vehicles that are commonly used for business purposes.
- Heavy-duty vehicles like semi-trucks or commercial trailers.
- Vehicles that employees drive on behalf of a business.
Keep in mind that every state and industry has different rules and regulations, so we also recommend looking up your local laws to avoid legal issues.
When Does Commercial Insurance Cover Vehicles?
Although business insurance covers a variety of risks discussed above, vehicle coverage is usually excluded. There are some cases where a BOP or general liability policy may offer some coverage for vehicles occasionally used for business purposes, but this is not common. Even in these cases, the coverage is usually limited and won’t cover vehicles that are used on a regular basis by the business.
With all this being said, businesses using vehicles in their operations regularly need specialized commercial automotive protection. Otherwise, you run the risk of paying out of pocket in the case of an accident.
What Does Commercial Auto Insurance Cover?
A commercial auto insurance policy provides complete coverage for vehicles utilized for business purposes. Typical coverage includes:
- Liability Coverage: This coverage protects against bodily harm or property damage if you are the driver at fault in an accident.
- Physical Damage Coverage: This coverage includes both collision and comprehensive coverages for vehicle damage. Collision insurance covers damage to your vehicle from hitting another object or vehicle, regardless of who’s at fault. Comprehensive coverage protects your vehicle from events outside of your control including theft, vandalism, fire, an animal being hit and more.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This policy protects your company if an employee is involved in an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver.
- Employee Coverage: Provides protection for employees who drive company-owned automobiles.
- Additional Coverage Options: To assure complete coverage, you can add services such as rental reimbursement and roadside assistance to your plan.
Do You Need Commercial Auto Insurance?
Deciding on whether or not your business needs commercial auto insurance depends solely on how vehicles are used within your daily operations. If the company uses vehicles for transportation, delivery, or regular travel, a commercial vehicle policy is essential. On the other hand, relying entirely on a personal auto policy for business purposes leads to big financial risks.
If you still aren’t sure about your business and it’s needs relating to auto coverage, ask yourself the following questions:
- Do you or your staff drive for business purposes?
- Is your personal vehicle routinely used for work-related purposes?
- Are there any company-owned vehicles in your fleet?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, commercial auto insurance is likely a good investment.

Protecting Your Business: Steps to Take
To guarantee that your business is properly insured, take the following steps:
- Examine your current insurance policy to detect any gaps in vehicle coverage.
- Assess your company’s vehicle usage to decide whether a commercial auto policy is required.
- Consult with an insurance agent to create a commercial auto insurance plan that is tailored to your specific business needs.
Final Thoughts
Commercial auto insurance is an important aspect of protecting your business, but typical business insurance policies tend to fall short. Whether you use personal cars for business or operate a fleet of commercial vehicles, you must have the proper insurance in place. Understanding the significance of commercial auto insurance can help you protect your organization from vehicle-related dangers and ensure your company is protected from all angles.
While researching and shopping for insurance policies can be daunting, it doesn’t have to be. Using EZ.Insure to compare quotes and coverage types makes the process easy. We offer side-by-side comparisons, so no matter how big or small your business is, they’ll be something for you. We also have a team of dedicated insurance professionals who are always on hand to walk you through the process. So take the next step in protecting your business and its assets today by visiting us at EZ.Insure. To get started, simply enter your ZIP code at the top of the screen or give us a call at 855-694-0047.